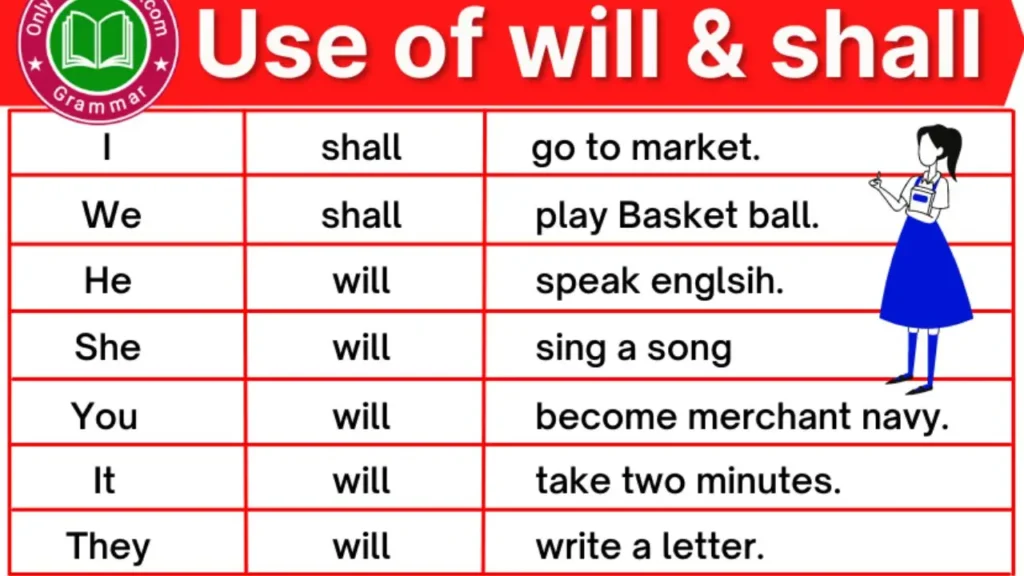
Difference Between Shall & Will: Prayer Shall is used with any first person subject (I or We) whereas “Will” is used with all other 2nd (second) or 3rd (third) person subjects.
Rules: –
Shall (first person):
- I shall attend the meeting tomorrow.
- We shall overcome this challenge.
Will (second person):
- You will receive your package by Friday.
- Will you join us for dinner tonight?
Will (third person):
- He will be there at 7 PM.
- She will not forget to bring the documents.
Shall (first person, expressing determination or intention):
- I shall do my best to help you succeed.
- We shall strive for excellence in our work.
Note:
Note that any emphatic structure will comes with the first person subject (I or We) while everything else comes in second/third person subjects.
Example:
- I will personally ensure the project is completed on time.
- You will receive your certificate after completing the course.
- She will deliver the keynote speech at the conference.
- We will support each other no matter what happens.
- Will you be attending the meeting tomorrow?
Uses:-
Rule 1 : To Show a simple futurity.
Example:
- She will visit her grandmother tomorrow.
- They shall complete the project by next week.
- He will start his new job on Monday.
- We shall meet at the usual place for lunch.
- The train will arrive at 7 PM tonight.
- I will send you the report by the end of today.
- They will attend the conference next month.
- He shall buy groceries on his way home.
- We will discuss the proposal in the meeting.
- She shall finish her homework before dinner.
Rule 2 : The Repetition of Sall or will is avoid in a Conditional sentence, It is replace by using Present Indefinite Tense with the Past that show condition.
Note: Note that the part stating the condition starts with if/when/unless/in case.
Example:
- If he arrives early, he finishes his work quickly.
- When they call me, I respond immediately.
- Unless you study hard, you fail the exam.
- In case it rains, we stay indoors.
- If she asks for help, I assist her.
- When they visit us, we prepare a special meal.
- Unless he apologizes, she forgives him.
- If they need assistance, we provide support.
- In case you have questions, feel free to ask.
- When she cooks, he cleans up afterwards.

Rule 3 : To know One’s Wishes
Example:
- Will you please pass the salt?
- Will he join us for dinner tonight?
- Will they attend the party tomorrow?
- Will she complete the assignment on time?
- Will you help me with this task?
- Will he buy a new car this year?
- Will they donate to the charity fundraiser?
- Will she visit her parents next weekend?
- Will you attend the meeting this afternoon?
- Will he take the day off on Friday?
Rule 4 : To make a Suggestion + Precaution With Else.
Example:
- You should ask someone else if he will help you with the project.
- We suggest finding another route in case the main road will be closed.
- I recommend contacting someone else if she shall not respond promptly.
- It’s advisable to bring someone else if he would not be available.
- She suggests calling someone else if he will not be able to make it.
- They propose waiting for someone else if she shall not arrive on time.
- It’s a good idea to call someone else in case he will not be able to attend.
- I suggest asking someone else if they shall be unable to assist.
- She recommends consulting someone else if he would not be able to come.
- It would be wise to inform someone else in case he will not be present.
Rule 5 : To Show Possibility
Example:
- If she had been more careful, she wouldn’t have made that mistake.
- If they had known about the delay, they would have left earlier.
- Had he been aware of the situation, he would have acted differently.
- She would have completed the project on time if she had had more resources.
- If I had been there, I would have helped you with the problem.
- If it had rained, the game would have been canceled.
- Had they arrived on time, they would have caught the train.
- She would have attended the meeting if she had been notified earlier.
- If he had studied harder, he would have passed the exam.
- Had she been more experienced, she would have handled the situation better.
Note: Please note that under the above situation, in the absence of vould, kud is used, in the absence of kud, shud is used and in the absence of shud, migh is also used.
Shall & Will In Tense
Present Tense:
- I/we shall (rarely used in simple present, more common in formal or legal contexts).
- You/they will (used for habitual actions or general truths).
Past Tense:
- I/he/she/we/they shall (rarely used in simple past).
- You/it will (used for past habitual actions or general truths).
Future Tense:
- I/we shall (used for simple future actions or intentions, especially in formal or literary contexts).
- You/he/she/it/they will (standard form for future actions or predictions).
Read Also:
- Difference Between Should & Would: Rules, Examples & Sentences
- Countable Noun क्या है? | Rules and Examples
- Use of Would: All Imformation, Rules, Examples & SentencesDifferent Between Can And Could: Rules, Examples & Sentences






