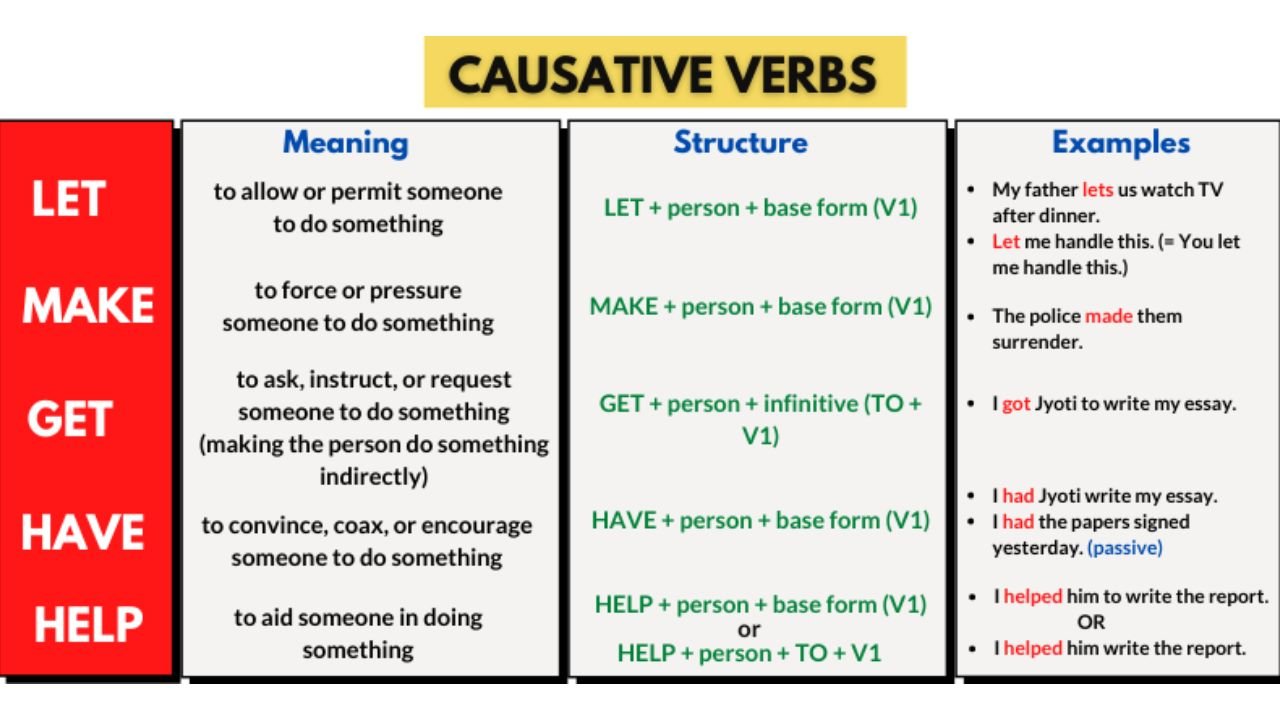
Causative Verb: A verb that is used to express that someone causes someone else to do something or causes something to happen.
According to uses causative is many divided into three part-
- Double Party Causative
- Triple Party Causative
- Multiple Party Causative
1. Double Party Causative
Double Party Causative: A construction in which one subject causes a second party to perform an action, which results in a third party or entity performing another action. It involves two stages of causation.
Key Features:
- First Party (Causer): Initiates the causative action or arrangement.
- Second Party (Intermediary): Performs the initial action or task.
- Third Party (Recipient or Final Action): Experiences or carries out the subsequent action resulting from the second party’s actions.
Note: Keep in mind that double party causative (object + V1) structure is used even after let, set, hear (sunna), see, notice (attention), hell, etc. verbs.
Example: I can’t let you go. / He set me free. / I heart in sing a song.
I had John wash the car.
- (I caused John to perform the action of washing the car.)
She got Mike to fix the leaky faucet.
- (She caused Mike to perform the action of fixing the leaky faucet.)
They had their neighbor mow the lawn.
- (They caused their neighbor to perform the action of mowing the lawn.)
He made his assistant deliver the package.
- (He caused his assistant to perform the action of delivering the package.)
We got the team to finish the report.
- (We caused the team to perform the action of finishing the report.)
2. Triple Party Causative
Triple Party Causative: A construction in which one subject causes a second party to perform an action, which then causes a third party to execute a subsequent action or achieve a final result. This involves three levels of causation.
Key Features:
- First Party (Causer): Initiates or arranges the overall sequence of actions.
- Second Party (Intermediary): Performs the initial action as directed by the first party.
- Third Party (Recipient or Final Action): Experiences or performs the subsequent action as a result of the second party’s actions.
Example: He gets me beaten in the class.
- He kept getting me beaten in the class.
- He can get me beaten in the class.
- He will get me beaten in the class.
- He can get me beaten in the class.
3. Multiple Party Causative
Multiple Party Causative: A grammatical structure where one subject causes multiple actions to be performed by different parties, or causes one party to arrange for another party to perform an action.
Key Features:
- First Party: Initiates the causative action or makes arrangements.
- Second Party: Performs the initial action.
- Third Party: May be involved in performing a subsequent action or review.
Example:
- He gets me a job.
- He is getting me a job by recommending.
Read Also: