Present Continuous Tense Definition: The change in verb according to time is called time and tense.
There are three types of time:
- Present Time
- Past Time
- Future Time
There are four types of tenses uses:
- Indefinite Tense
- Continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense: A grammatical tense used to describe actions that are currently in progress, temporary situations, or planned future events. It is formed using the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the base form of the main verb plus the -ing ending.
Such sentences which do not show the past or future but show the present time and the work is happening in the present.
Rule: S + is/am/are + V4 + O
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| i – am | You – are |
| He – is | We – are |
| She – is | They – are |
| it –is | It’s – are |
| Name – is | Names – are |
| This– is | These – are |
| That – is | Those – are |
Rule and Uses:
[1.] To show a present continued action.
Example:
- She is studying for her exams right now.
- They are working on the new project at the moment.
- He is reading a book in the library.
- The kids are playing in the park this afternoon.
- I am cooking dinner while listening to music.
[2.] To show a present moment habitual action.
Example: Now a days he drinks wines. (x) / Now a days he is drinking wines. (✓)
- Nowadays, she is practicing yoga every morning.
- These days, he is commuting to work by bike.
- At present, they are attending a weekly book club.
- Currently, I am studying for my final exams.
- This week, she is volunteering at the local animal shelter.
[3.] To make a present momentary action.
Example:
- He is sitting and I am standing.
- She is talking on the phone while he is reading the newspaper.
- They are eating breakfast and the dog is sleeping under the table.
- I am waiting here and you are arriving soon.
- The kids are playing outside while their parents are chatting.
[4.] To show of 50% certain future plane.
Example:
- He is buying a new car next month.
- We are traveling to Italy next summer.
- She is moving to a new apartment next week.
- They are starting a new business soon.
- I am joining a cooking class next semester.
[5.] To show the nearest plane.
Example:
- Now, I am going to sing a song on the stage.
- I am meeting my friend for coffee shortly.
- We are having dinner together this evening.
- She is presenting her project in the next hour.
- They are going to the concert tonight.
[6.] Now, This time, These, Those, At present, At the moment, Currently etc can be used in this tense with continued action.
Example: This day he teaches physics. (x) / This days he is teaching physics. (✓)
- This week, he is teaching physics.
- Currently, she is working on a new novel.
- At the moment, they are renovating their house.
- These days, I am focusing on my fitness.
- This month, we are hosting a series of workshops.
[7.] Always, Never, Seldom, Often, Rearly, Occasionally, Usually etc not uses in this tense with habitual actions.
Example: He is always coming let. (x) / He always come let. (✓)
- He always arrives late to meetings.
- She never forgets to call her parents.
- They usually go for a walk in the evening.
- I rarely eat fast food.
- We often visit our grandparents on weekends.
[8.] A verb of perception or static verb show its continuous sense in indefinite structure.
(Appear, Seem, Look, Happen, Late, Understand, Hope, Think, Deny, See, Hear, Notice, Presume, No, Like, Love etc)
Example: I am knowing it. (x) / I know it. (✓)
- I understand the problem.
- She likes the new restaurant.
- They know the answer to the question.
- He hopes to get a promotion.
- We see the changes clearly.
Present Perfect tense in Sentences
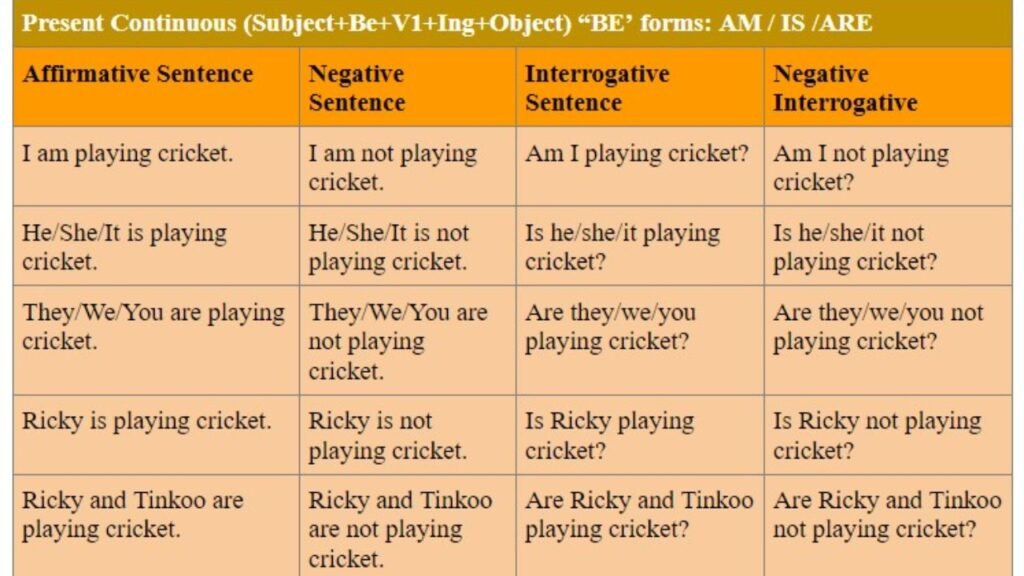
Affirmative Sentences:
A sentence which expresses a fact or claim. A sentence which has a meaning or some action is happening.
- She reads books.
- They play football.
- He eats fruit.
- I study English.
- We go to school.
- They speak French.
- She teaches Mathematics.
- He works in an office.
- It rains in summer.
- The dog barks loudly.
Negative Sentences:
A sentence which denies the existence or occurrence of something. Which gives a sense of no, i.e. refusal to do any work.
- She does not read books.
- They do not play football.
- He does not eat fruit.
- I do not study English.
- We do not go to school.
- They do not speak French.
- She does not teach Mathematics.
- He does not work in an office.
- It does not rain in winter. –
- The dog does not bark at night.
Interrogative Sentences:
The sentence which asks a question and has a question mark in it.
- Does she read books?
- Do they play football?
- Does he eat fruit?
- Do I study English?
- Do we go to school?
- Do they speak French?
- Do she teach Mathematics?
- Do he work in an office?
- Does it rain in summer?
- Does the dog bark loudly?
Assertive Sentences:
A sentence which expresses a statement or states a fact.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The sun rises in the east.
- Birds chirp in the morning.
- Computers are useful machines.
- Plants need sunlight to grow.
- English is spoken in many countries.
- The Earth revolves around the sun.
- Fish live in water.
- The moon shines at night.
- Elephants are large animals.
Exclamatory Sentences:
A sentence that expresses strong emotion or excitement and ends with an exclamation mark.
- What a beautiful flower this is! – What a beautiful flower it is!
- What delicious food they cook!
- What an interesting story that was!
- What a talented singer she is!
- What a loud noise it makes!
- What a hot day it is today!
- What a funny joke you told!
- What an amazing view!
- What a long journey it was!
- What a surprise this party is!
FAQ: Present Continuous Tense
1. What is the Present Continuous Tense?
- The Present Continuous Tense, also known as the Present Progressive Tense, describes actions that are currently happening at the moment of speaking or actions that are ongoing around the present time. It can also indicate future plans or temporary actions.
2. How is the Present Continuous Tense formed?
- The Present Continuous Tense is formed using:
- Subject + am/is/are + verb(-ing)
- Example: She is eating lunch.
3. When should I use the Present Continuous Tense?
- Use the Present Continuous Tense:
- For actions happening right now: She is reading a book.
- For temporary actions around the present time: He is staying with friends this week.
- For future plans: They are traveling to Paris next month.
- For actions in progress over a period of time: I am working on a new project.
4. Can you give examples of Present Continuous Tense sentences?
- Affirmative:
- I am studying for my exams.
- They are playing soccer in the park.
- Negative:
- She is not watching TV right now.
- We are not attending the meeting today.
- Questions:
- Are you coming to the party tonight?
- Is he working on the report?
5. How do you form negative sentences in the Present Continuous Tense?
- Subject + am/is/are + not + verb(-ing)
- Example: He is not working today.
6. How do you form questions in the Present Continuous Tense?
- Am/Is/Are + subject + verb(-ing)?
- Example: Are they playing basketball?
7. What are some common time expressions used with the Present Continuous Tense?
- Common time expressions include:
- Now: I am studying now.
- Currently: She is currently working on her thesis.
- At the moment: They are eating dinner at the moment.
- This week/month/year: We are visiting relatives this month.
8. Can the Present Continuous Tense be used with adverbs of frequency?
- Typically, adverbs of frequency (e.g., always, usually, often) are not used with the Present Continuous Tense when referring to habitual actions. They are generally used with the Present Simple Tense instead.
- Incorrect: He is always arriving late.
- Correct: He always arrives late.
9. Can the Present Continuous Tense be used with stative verbs?
- No, stative verbs (e.g., know, like, love, understand) are generally not used in the Present Continuous Tense because they describe states rather than actions.
- Incorrect: I am knowing the answer.
- Correct: I know the answer.
10. How is the Present Continuous Tense different from the Present Simple Tense?
- Present Continuous Tense: Describes actions happening right now or temporary situations.
- Example: She is cooking dinner.
- Present Simple Tense: Describes habitual actions, general truths, or regular occurrences.
- Example: She cooks dinner every evening.
11. Can the Present Continuous Tense be used for future arrangements?
- Yes, the Present Continuous Tense can be used to talk about scheduled or planned future events.
- Example: I am meeting my friend tomorrow.
12. Are there any exceptions or special cases for using the Present Continuous Tense?
- While the Present Continuous Tense is generally used for ongoing actions and temporary situations, it is important to remember that it is not used with stative verbs and is not typically used with adverbs of frequency for habitual actions.
Read Also:






